

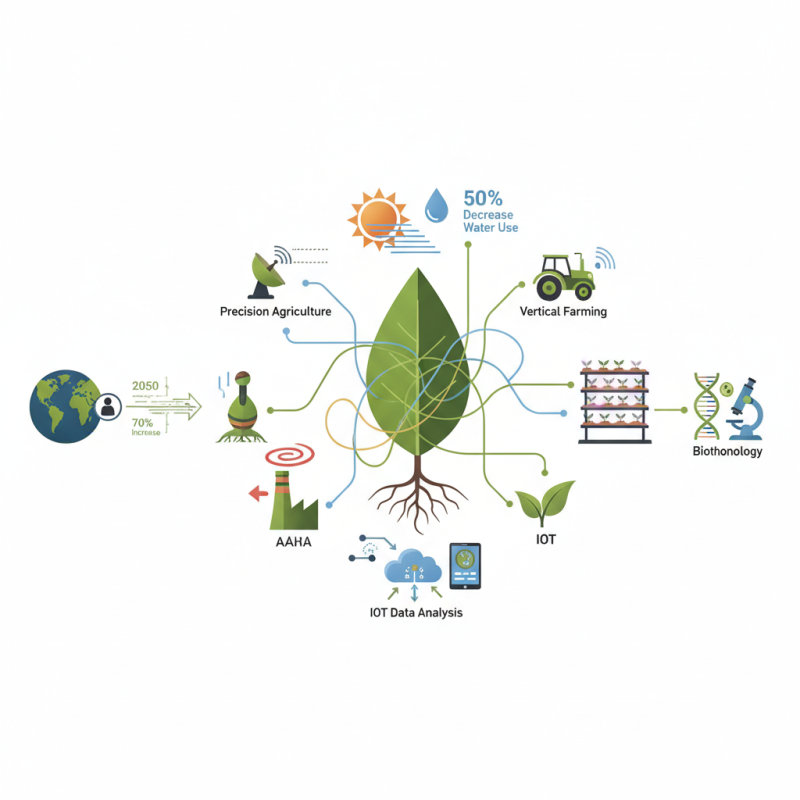
The intersection of technology and sustainable food production is becoming increasingly vital as the world grapples with a growing population and diminishing natural resources. As projected by the United Nations, the global population is expected to reach approximately 9.7 billion by 2050, necessitating a staggering 70% increase in food production by that time. This places an immense pressure on agricultural systems to adapt and innovate, making the integration of technology in food production not just beneficial, but essential.
Emerging technologies such as precision agriculture, vertical farming, and biotechnology are paving the way for more sustainable practices that can reduce resource consumption and environmental impact. According to a report by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), implementing responsible agricultural technologies can lead to a 50% decrease in water use and a significant reduction in greenhouse gas emissions while maintaining crop yields. Furthermore, the adoption of Internet of Things (IoT) solutions in farming can enhance real-time data analysis, leading to better decision-making and efficiency improvements that align with sustainability goals.
As we delve into the various ways to harness technology in food production, it is crucial to examine how these innovations not only address present challenges but also build a resilient agricultural system for future generations. Embracing these advancements will play a pivotal role in creating a sustainable food ecosystem capable of meeting the demands of a burgeoning populace while safeguarding our planet's resources.

Sustainable food production is a critical approach to addressing the challenges posed by climate change, resource depletion, and food security. At its core, sustainable food production refers to methods that utilize natural resources in ways that ensure both ecological balance and societal well-being. By focusing on practices that preserve the environment, such as crop rotation, permaculture, and organic farming, we can enhance biodiversity while reducing the carbon footprint associated with food production. Understanding these techniques is essential, as they not only support healthier ecosystems but also improve the resilience of agricultural systems against environmental stresses.
The importance of sustainable food production cannot be overstated. As the global population continues to grow, the demand for food will increase, necessitating innovations that minimize waste and utilize resources efficiently. Embracing sustainable practices helps mitigate issues like soil degradation, water scarcity, and reliance on chemical fertilizers, which can harm ecosystems and human health. Additionally, sustainable food production fosters community engagement and supports local economies through the promotion of local food systems. Ultimately, this approach is vital for securing a food supply that meets current needs without compromising the ability of future generations to thrive.
The integration of technology in agriculture and food production is transforming the way food is cultivated, processed, and distributed. Precision agriculture, for instance, utilizes data analytics and satellite imagery to optimize crop yields while minimizing resource usage. Farmers can monitor soil health, moisture levels, and crop conditions in real-time, enabling them to make informed decisions that enhance productivity and sustainability. By harnessing these advanced technologies, agricultural practices can become more efficient, reducing waste and environmental impact.
In addition to precision agriculture, innovations such as vertical farming and hydroponics are reshaping traditional food production methods. These techniques allow for the cultivation of crops in controlled environments, using significantly less water and land than conventional farming. Furthermore, the use of automation and robotics in planting, harvesting, and processing increases efficiency and reduces labor costs. The application of biotechnology in developing drought-resistant and pest-resistant crops also plays a crucial role in ensuring food security amidst climate change challenges. Together, these technological advancements are paving the way for more sustainable food systems that can meet the growing global demand while preserving the planet's resources.
Innovative technologies are transforming sustainable food production by significantly enhancing crop yield and efficiency. One notable development is precision agriculture, which utilizes data analytics and IoT devices to optimize farming practices. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), implementing precision farming techniques can increase crop productivity by up to 20%. By analyzing soil health, weather conditions, and crop requirements, farmers can make better-informed decisions, reducing waste of resources such as fertilizers and water.
Furthermore, vertical farming is emerging as a revolutionary method in urban agriculture. This innovative approach allows for the cultivation of crops in controlled indoor environments, using less land and resources compared to traditional farming. A report by the International Society for Horticultural Science indicates that vertical farming can yield 10 to 20 times more produce per square meter than conventional methods. By employing hydroponics or aeroponics, these systems minimize water usage by up to 90% while eliminating the need for pesticides, aligning closely with sustainable practices.
Finally, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning in agriculture is allowing for enhanced crop management and disease prediction. Research from McKinsey indicates that AI-driven technologies can improve crop yields by an additional 15% and boost global agricultural productivity significantly. By enabling farmers to quickly identify and address potential issues in real-time, these technologies not only enhance yield but also contribute to long-term sustainability in food production.
| Technology | Description | Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Precision Agriculture | Utilizes GPS and IoT sensors to monitor crop health and soil conditions. | Increases yield and reduces waste by optimizing resource usage. | High initial costs and requires significant training. |
| Hydroponics | Soil-less growing method using nutrient-rich water solutions. | Reduces water usage and allows for year-round crop production. | Requires careful monitoring and can be expensive to set up. |
| Drones | Aerial imagery capture and analysis for crop monitoring. | Provides real-time data and aids in making informed decisions. | Regulatory issues and potential for technical failures. |
| Vertical Farming | Growing crops in stacked layers to optimize space. | Maximizes urban space and reduces transportation emissions. | Energy-intensive and requires advanced technology. |
| Artificial Intelligence | Data analysis and predictive modeling for crop management. | Increases efficiency and aids in pest management. | Data privacy concerns and high implementation costs. |
Precision agriculture represents a revolutionary approach to food production, merging advanced technology with sustainable practices. By utilizing data analytics, satellite imagery, and IoT devices, farmers can monitor and manage their crops with unparalleled accuracy. This method allows for the precise application of water, fertilizers, and pesticides, significantly reducing waste and minimizing environmental impact.
Tips for implementing precision agriculture include starting with soil health assessments to understand your land's specific needs. Investing in smart sensors can help in real time monitoring, guiding decisions on irrigation and nutrient management. Additionally, using drones for aerial imagery can provide insights into crop health, allowing for targeted interventions rather than blanket treatments.
Moreover, integrating crop rotation and cover cropping into your precision agriculture plan can enhance soil structure and biodiversity. By analyzing yield data, farmers can make informed decisions on crop selection and optimize planting schedules based on climatic conditions. This synergy of technology and traditional practices ensures a more resilient agricultural system while supporting sustainable food production.
Data analytics is transforming the landscape of sustainable food systems by enabling farmers and producers to make informed decisions based on real-time information. By collecting and analyzing data on soil health, weather patterns, and crop performance, stakeholders can optimize resource use and improve yield quality. For instance, precision agriculture techniques utilize sensors and satellite imagery to monitor fields meticulously, allowing farmers to apply water and fertilizers only where they are needed, thus minimizing waste and environmental impact.
Moreover, data analytics facilitates supply chain transparency, helping to reduce food waste and enhance traceability. By analyzing consumption patterns and predicting demands, food producers can adjust their production strategies accordingly, preventing overproduction and surplus that often leads to waste. Additionally, insights gained from consumer preferences through data mining can guide farmers to grow crops that are not only environmentally sustainable but also aligned with market needs.
This integration of data-driven approaches cultivates a more responsive and responsible food production system, promoting sustainability throughout the entire supply chain.





