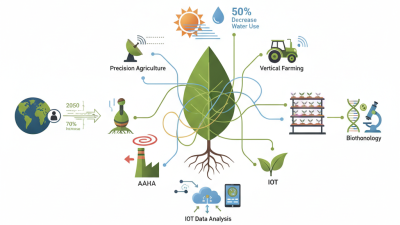
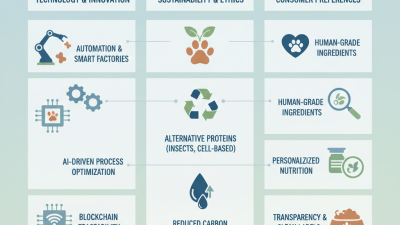
In the ever-evolving landscape of agriculture, "technology in food production" is reshaping how we grow and distribute our food. Dr. Emily Carter, a renowned expert in agricultural technology, once stated, "Innovation in farming not only boosts efficiency but also addresses sustainability challenges." This sentiment is more relevant than ever.
Modern advancements bring both promise and complexity. Precision farming tools, data analytics, and automation can significantly enhance productivity. However, many farmers face challenges in adopting these technologies. Limited resources and a lack of training can hinder progress. The gap between innovation and practical application poses a problem that needs addressing.
Yet, success stories abound. Farms employing drones for crop monitoring and smart sensors for irrigation are witnessing impressive results. By embracing technology in food production, we can envision a future where efficiency meets sustainability. Still, it’s essential to recognize that not all technologies will fit every operation seamlessly. A careful evaluation of what works best is crucial for effective implementation.
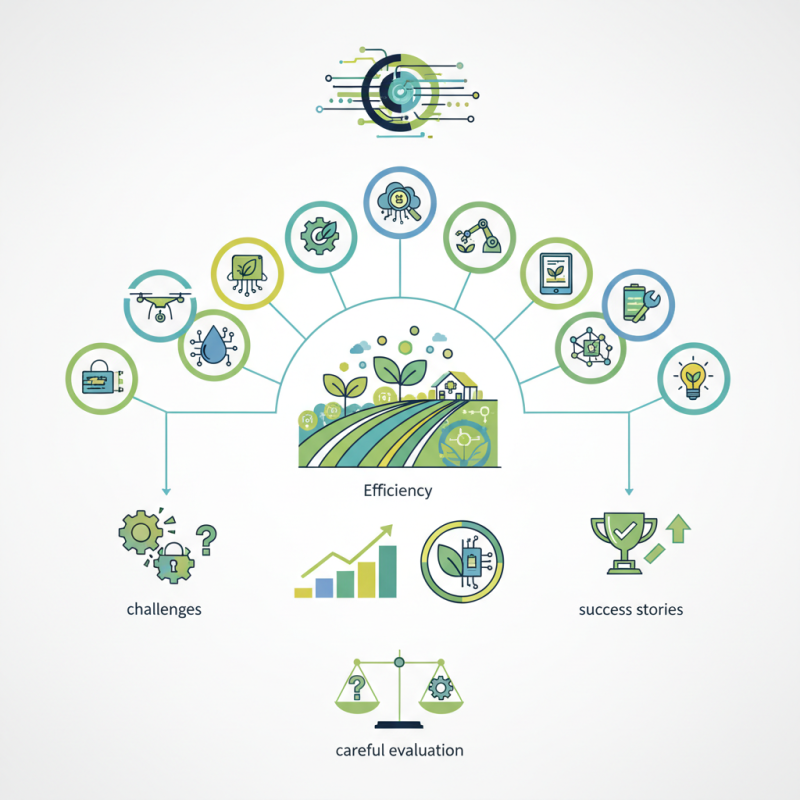
Automation tools are reshaping food production. These tools can streamline processes, reduce waste, and save time. Imagine a conveyor system that automatically sorts fruits and vegetables. This system can improve accuracy and speed. Workers can focus on quality checks instead of manual sorting.
Using data analytics is another way to enhance efficiency. By tracking production trends, companies can forecast demand more accurately. However, data management can be complex. Many producers struggle with integrating new technology. Adapting to changes requires training and time. It’s crucial to involve teams in the transition.
Robotics in packaging also plays a vital role. Automated packing can reduce labor costs. Yet, relying too heavily on machines might lead to job losses. Striking a balance is essential. Companies must find ways to coexist with technology while ensuring job security for workers. The potential is immense, but careful implementation is key.
| Tip | Description | Expected Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Implement IoT Devices | Utilize Internet of Things devices for real-time monitoring of food production. | Increased transparency and data-driven decision making. |
| 2. Use Automated Packaging Systems | Integrate machinery for automated packaging to enhance speed. | Reduced labor costs and improved packaging consistency. |
| 3. Adopt Cloud-based Solutions | Utilize cloud computing for data storage and collaboration. | Enhanced access to information and improved teamwork. |
| 4. Utilize Artificial Intelligence | Implement AI for predictive analytics in supply chain management. | Optimized inventory and reduced waste. |
| 5. Incorporate Robotics for Processing | Adopt robots for repetitive tasks in food processing. | Increased efficiency and reduced error rates. |
| 6. Implement Blockchain for Traceability | Use blockchain technology for tracking food products. | Improved food safety and compliance. |
| 7. Optimize Supply Chain with Software | Utilize software tools for managing supply chain logistics. | Increased efficiency and lowered costs. |
| 8. Use Data Analytics for Insights | Apply data analytics to identify trends in production. | Informed strategic decisions and optimized operations. |
| 9. Integrate E-commerce Platforms | Utilize e-commerce for direct sales to consumers. | Expanded market reach and increased sales. |
| 10. Enhance Quality Control with Tech | Use technology for quality assurance in production. | Consistent product quality and customer satisfaction. |
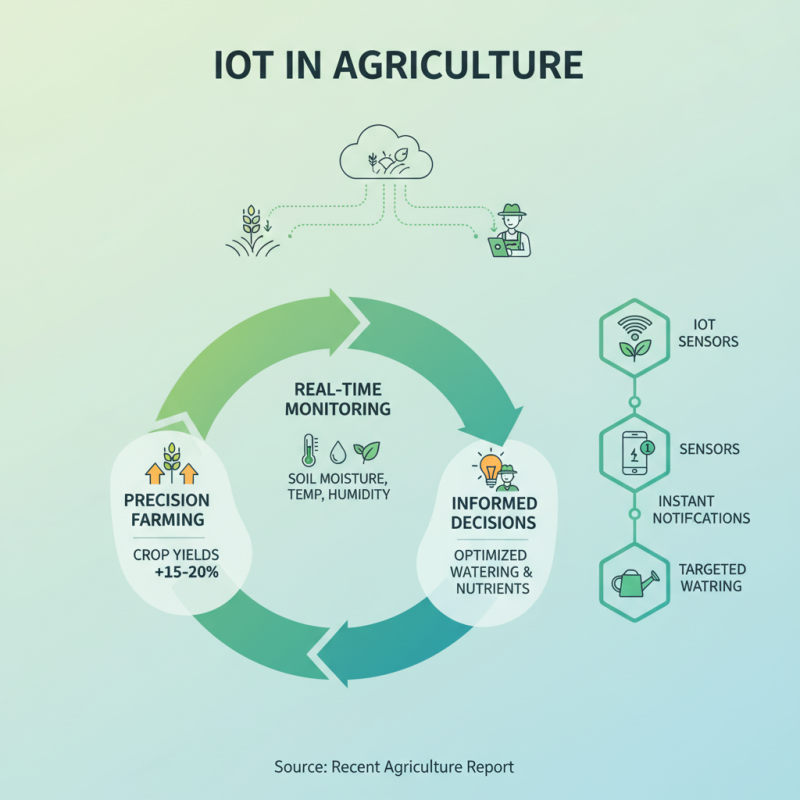
The integration of IoT solutions in agriculture is transforming food production. According to a recent report, precision farming can boost crop yields by 15-20%. Real-time monitoring of soil moisture, temperature, and humidity allows farmers to make informed decisions. For instance, IoT sensors can notify farmers when specific crops require watering.
Tip: Invest in soil moisture sensors. They help farmers understand when to irrigate, reducing water waste. By using IoT technology, farms can become 20% more efficient. This efficiency not only saves resources but also leads to higher crop quality.
However, the transition to smart farming is not without challenges. Some farmers struggle with technology adoption. Access to reliable internet in rural areas remains an issue. Training workers to use advanced tools is another hurdle. Despite these challenges, the potential for increased productivity is significant. Embracing IoT could reshape the agricultural landscape, yielding benefits that are hard to overlook.
In modern agriculture, data analytics plays a vital role in enhancing crop yield and managing resources efficiently. Farmers can collect data on soil conditions, weather patterns, and plant health. This information helps in making informed decisions about irrigation and fertilization. For instance, analyzing moisture levels can determine the best times to water crops, reducing waste.
However, not all data usage leads to positive outcomes. Sometimes, farmers rely too much on technology without understanding the underlying data. Misinterpretation can lead to over-fertilization, harming plants and the environment. It's essential to blend technology with traditional knowledge for the best results. Tracking crop performance also presents challenges. Data overload can make it hard to focus on what truly matters.
To effectively utilize technology, farmers must develop a clear strategy. Identifying key performance indicators is crucial. This helps in determining what data to prioritize. Additionally, ongoing education and adaptation are necessary. As technology evolves, so do the best practices. Reflecting on past experiences can provide valuable insights for future improvements. Balancing technology and traditional methods is a journey worth exploring.
In the food production sector, robotics are transforming how tasks are carried out. These machines are designed for speed and precision. They can sort, package, and even harvest crops. The integration of robotics reduces labor costs and eliminates repetitive strain injuries for workers. These changes boost overall efficiency and output.
However, the transition to robotics isn't without challenges. Training staff to operate and maintain these machines can be complex. Some workers may feel threatened by automation, worrying about job security. Additionally, initial setup costs for robotic systems can be high. Companies must evaluate whether the long-term benefits outweigh these challenges.
Despite these hurdles, the potential gains in productivity are substantial. Robotics can ensure consistent quality in food production. They can work in conditions that are unsuitable for human workers. With the right approach, addressing concerns about automation can lead to a smoother integration. Embracing robotics requires a mindset shift, but the benefits could be worth it.
This chart showcases the improvement in labor efficiency in food production facilities after adopting robotics over the past few years. The data illustrates a steady increase in efficiency from 60% in 2020 to 90% in 2023.
Sustainable technology in food production is gaining traction. It helps reduce waste and improve efficiency. Innovations like precision agriculture use data to optimize crop yields. This technology minimizes resource use while maximizing output. For example, sensors can monitor soil moisture, allowing farmers to irrigate more effectively. This not only saves water but also enhances crop health.
However, implementing these technologies isn't always seamless. Some farmers struggle with the learning curve of complex systems. Not all regions have access to advanced tools, creating a digital divide. Additionally, integrating new technologies requires investment, which can be a barrier for smaller operations.
It’s essential to reflect on these challenges. Finding ways to support all producers in adopting sustainable practices is crucial for a truly eco-friendly food system. Balancing efficiency and sustainability is a continuous journey that requires commitment and adaptation.